Since the last decade, when the term ‘Big Data’ was coined and until today, the term has remained an enigma to most people. In 2005, Roger Mougalas from O’Reilly Media coined the term Big Data for the first time. However, the usage of Big Data and why do we need to understand data has been around much longer.
Gartner’s definition (which is still one of the go-to definitions) of Big Data is as follows:
“Big data is high-volume, high-velocity and/or high-variety information assets that demand cost-effective, innovative forms of information processing that enable enhanced insight, decision making, and process automation.”
These are the 3 V’s of Big Data: Volume, Velocity and Variety.
- Volume: It refers to the vast amount of data generated every second.
- Velocity: It refers to the speed at which data is generated and the speed at which it moves around.
- Variety: It refers to the different types of data we can use these days.
In addition to these 3 V’s, there are 2 V’s which is a necessity today. They are:
- Veracity: It refers to the trustworthiness of the data. This means it allows us to know whether the data that is being stored and mined is meaningful to the problem that is being analyzed.
But, all the volumes of data generated with a high velocity which are of different variety and veracity have to be turned into Value.
- Value: It refers to our ability to turn our data into value.
[Note:Yes, beginners like me, shall get confused while referring to different websites seeing them claiming different numbers of characteristics(or V’s) of Big Data. My interpretation of the varying number of V’s is that each characteristic mentioned by other websites carry their own importance. As data is generated at different industries and work sectors, each of them has its own patterns and ways to see them. Big Data can mean so many different things to so many different people. Hence, we come up with various characteristics which can hold more importance the other.]
The term ‘Big Data’ has been authored to refer to the extensive amount of data that cannot be managed by traditional data-handling methods or techniques. The field of Big Data plays a highly compelling role in diverse fields such as agriculture, banking, education, finance, marketing, healthcare, etc.
Big data analytics examines large amounts of data to uncover hidden patterns, correlations and other insights. With today’s technology, it’s possible to analyze your data and get answers from it almost immediately – an effort that’s slower and less efficient with more traditional business intelligence solutions.
Here is why Big Data Analytics is important,
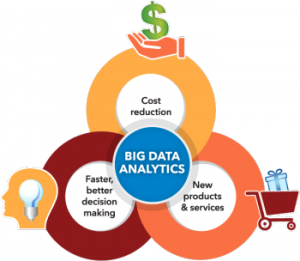
Source: www.sas.com
There has been a perpetually expanding interest for big data because of its rapid growth,development and because it is able to cover different sectors of applications.
Apache Hadoop is an open source technology for storage and large scale processing of data-sets on clusters of commodity hardware. It is licensed under the Apache License 2.0. It allows the distributed processing of large data sets across clusters of computers using simple programming models. It is designed to scale up from single servers to thousands of machines, each offering local computation and storage. Data of all formats such as structured, semi-structured and unstructured data can be processed and stored in this framework.
Hadoop Framework is divided into Master-Slave architecture. The 2 components of the framework:
- In the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) layer, the Name Node is the master component while the Data Node is the Slave component.
- In the MapReduce layer, the Job Tracker is the master component while the Task Tracker is the slave component.

